Charlie Kestler, one of CCLP’s Policy Fellows, provided testimony in support of Senate Bill 24-211, Adjustments to the Necessary Document Program. CCLP is in support of SB24-211, as it is one of our priority bills.
Recent articles
CCLP testifies in support of protections for DNC drivers
Charles Brennan provided testimony in support of House Bill 24-1129, Protections for Delivery Network Company Drivers. CCLP is in support of HB24-1129.
CCLP testifies in support of TANF grant rule change
CCLP's Emeritus Advisor, Chaer Robert, provided written testimony in support of the CDHS rule on the COLA increase for TANF recipients. If the rule is adopted, the cost of living increase would go into effect on July 1, 2024.
CCLP testifies in support of updating protections for mobile home park residents
Charles Brennan provided testimony in support of House Bill 24-1294, Mobile Homes in Mobile Home Parks. CCLP is in support of HB24-1294.
Bill would help people with disabilities get help
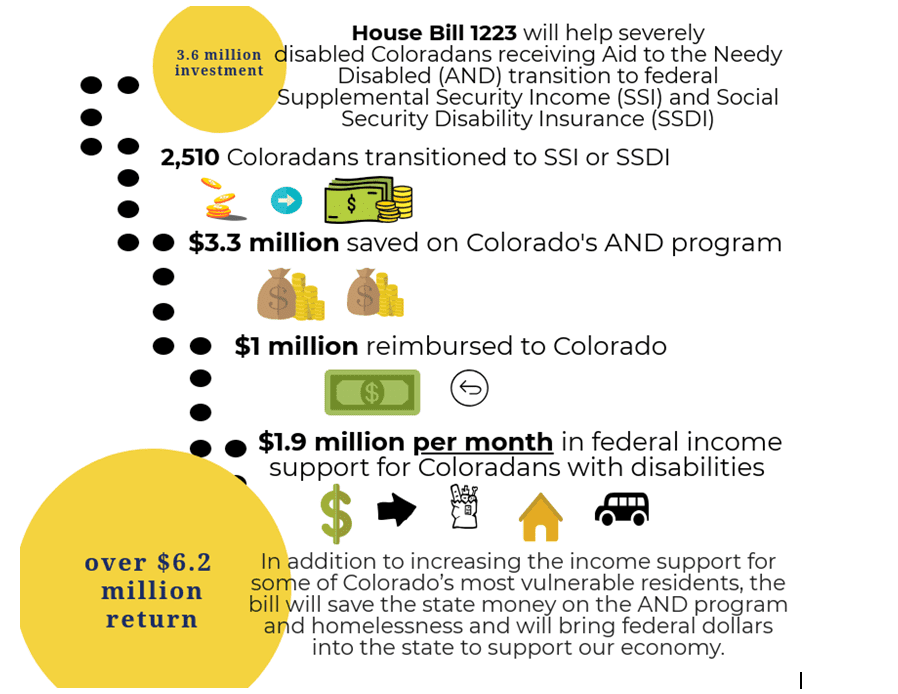
No person should have to live on the streets, go hungry, or end up in jail because they have a disability that prevents them from earning an income that supports their basic needs. Conditioning access to basic needs on earning an income is one way our society deprives people with disabilities of the opportunity to live their healthiest, most fulfilling lives possible; and this is made worse by the fact that we make programs designed to mitigate that injustice inaccessible to the people that need them most.
Supplemental Security Income (SSI) and Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) are federal programs that help people with disabilities meet their needs by providing them with monthly income support. The current SSI benefit amount is $771 per month. The SSDI benefit varies based on the recipient’s work history but the average benefit for an individual is $1,197 per month. (An individual who is eligible for a smaller benefit under SSDI can use SSI to bring their benefit up to $771 a month). SSI and SSDI help people with disabilities obtain housing, get enough food to eat, and maintain the stable circumstances they need to experience recovery.
Unfortunately, for many severely disabled individuals, the federal relief is either long-delayed or simply unobtainable. The problem is the complex application process, which requires detailed documentation of deeply personal mental and physical health issues on up to 14 different forms that require specialized knowledge to complete adequately. The cumbersome process also requires applicants to record up to 15 years of work history and at least two years of medical treatment history. Furthermore, applicants are required to stay in contact with the Social Security Administration (SSA) — which is difficult for clients that don’t have a phone or a home. Failure to communicate, attend an appointment, or provide sufficient information will often result in a denial of benefits regardless of the individual’s actual level of impairment.
The process is challenging for anyone who is not trained to complete it successfully; for those with serious mental illness and people who are homeless, it is hard to even know where to begin. It is no wonder that less than 30 percent of initial SSI/SSDI applications submitted without navigation assistance are successful. And for homeless applicants that number is only 10-15 percent. While about half of the cases that are denied at the initial level are approved on appeal, many applicants simply give up. If they choose to proceed, the appeal process can take more than a year to resolve. In fiscal year 2016, 8,699 Americans died waiting for their disability case to be resolved. In fiscal year 2017, that number rose to 10,002.
Support HB 1223
House Bill 1223 invests in an obvious and proven solution to this problem: SSI and SSDI application assistance. As a result of the bill, client advocates that know and understand SSA’s criteria for disability will be available to help SSI and SSDI applicants navigate the application process and develop strong SSI/SSDI applications. The client advocates will help applicant’s understand the process, gather the necessary documentation, and keep track of necessary appointments. They will also be able to serve as client representatives, providing a consistent point of contact for the SSA when that is needed.
The bill targets those with the greatest need by providing application assistance to recipients of Aid to the Needy Disabled (AND). AND uses state and some county funds to provide just $217 a month to people with severe physical or mental disabilities that prevent them from working. With only $217 per month in income many AND clients are homeless, many do not have access to reliable transportation, and most do not have the stable circumstances they need to attend to their significant health challenges. These individuals are in no position to complete the cumbersome SSI and SSDI application process; though they often need the support the most.
HB 1223 would increase access to application assistance in Colorado and thereby increase the income support for Coloradans with severe disabilities by over three times from $217 per month from state and local revenue to at least $771 per month from federal dollars. People need these resources to help them pay for basic needs like housing, food, and transportation, and with the resources, many are able to experience significant health improvement. A handful of nonprofits, such as Easter Seals and Bayaud Enterprises, provide similar assistance but their reach and resources are limited.
In a small pilot program authorized in Colorado in 2014, 54 percent of cases were approved and clients were connected to benefits in an average of six months from the initiation of the application process – a dramatic improvement from those applying outside of the pilot without assistance. Similar programs in other states have seen even better results.
In addition, the program will generate a large return on investment by increasing the approval rate for SSI and SSDI. When an AND clients is approved for SSI, the SSA reimburses the state for AND payments made to that individual. HB 1223 will increase the number of clients for whom the state receives reimbursement. HB 1223 will also reduce the number of AND payments the state has to make in the first place by reducing the amount of time people spend on the AND program. In addition, SSI and SSDI recipients use their federal support to pay rent to local landlords, buy food and other necessities at local stores, and transportation on local transit or gas at local stations. As a result, all of those federal dollars will be cycled through our Colorado economy.
As a result of the reimbursements and savings connected to AND and the increased income for Coloradans with disabilities, CCLP estimates that Colorado could realize a $6.2 million return from a $3.6 million investment in application assistance. The program will also reduce local spending on homeless services, emergency-room care, and public safety by supporting stability for many of Colorado’s most vulnerable residents.
The things we pay for with taxes reflect the values we hold as a society. We should support access to basic needs for our neighbors with severe disabilities because it is the just thing to do. But, as is often the case, investing in the well-being of our neighbors also happens to be the most financially responsible thing to do too.
-By Allison Neswood





